Project Description
The project aims to deploy a web application using Docker Swarm, a container orchestration tool that allows for easy management and scaling of containerized applications. The project will utilize Docker Swarm's production-ready features such as load balancing, rolling updates, and service discovery to ensure the high availability and reliability of the web application. The project will involve creating a Dockerfile to package the application into a container and then deploying it onto a Swarm cluster. The Swarm cluster will be configured to provide automated failover, load balancing, and horizontal scaling to the application. The goal of the project is to demonstrate the benefits of Docker Swarm for deploying and managing containerized applications in production environments.
Docker Swarm setup
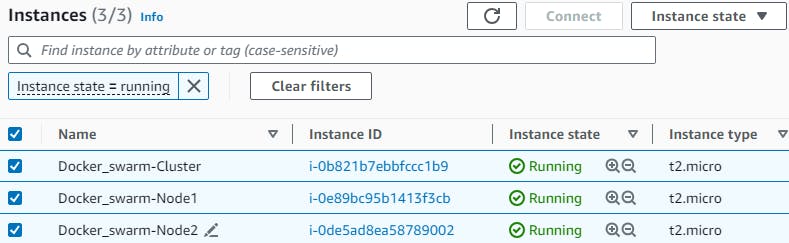
Log in to the AWS console and create 3 EC2 instances
Docker_swarm-Cluster
Docker_swarm-node1
Docker_swarm-node2
In all three instances, inside the inbound rules, allow
Custom TCP — 2377 — Anywhere IPv4 (Used for connection between master and nodes)
Custom TCP — 8001 — Anywhere IPv4 ( Django application port number )
Install docker with docker engine on al
Connect to all the instances and install the docker
sudo apt install docker.io
Now on the “Docker_swarm-Cluster” and run the below command,
sudo docker swarm init
This command generates a token that can be used to join work nodes to this cluster
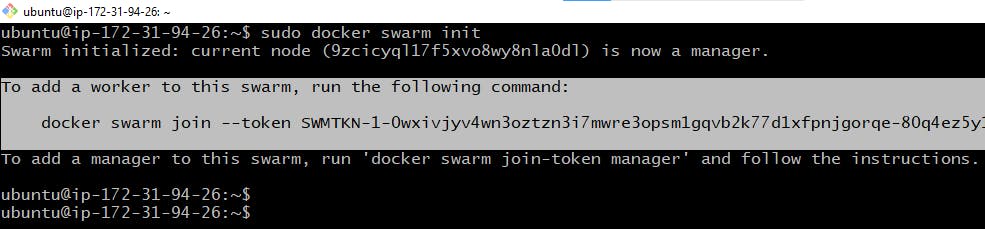
After initializing the swarm on the “Docker_swarm-Cluster”, a join token is generated to add other nodes into the swarm as a worker. Copy and run the key on the worker nodes.
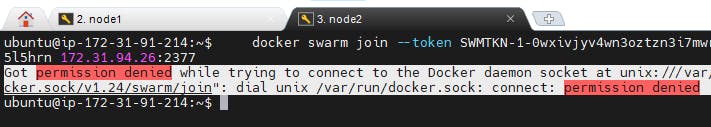
To overcome this error use sudo privileges
or
Run the below command on all the nodes
# Add the user to the docker group and reboot
$ sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
$ sudo reboot
Generate the token again
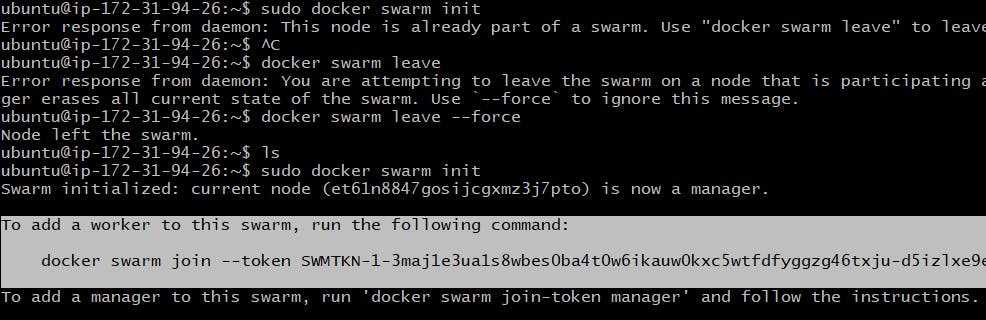
Paste the token on worker nodes

On the Master node
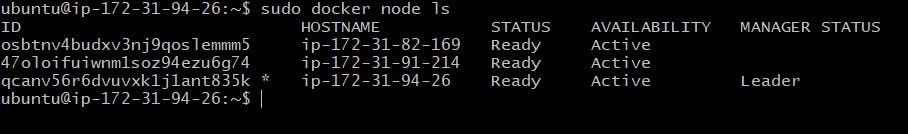
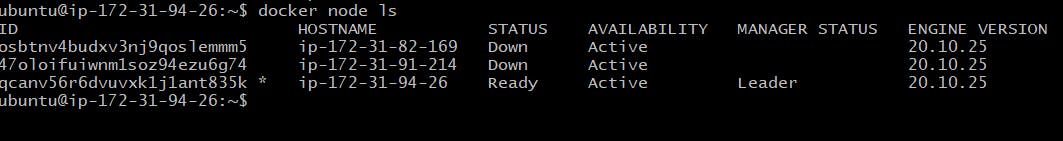
# Check the list of node attached to Cluster swarm
$ sudo docker node ls
Type to run some docker commands on the Master node
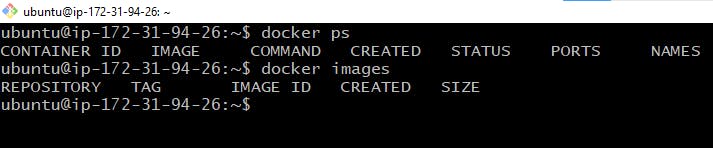
# List the docker containers
$ sudo docker ps
# List the docker images
$ sudo docker images
If we use the docker run command then our application will be executed only in one container.
In docker swarm, we need to deploy our application as a service.
Service is the collection of one or more containers of the same image.
Now, on Cluster Node (Leader) we will create a service
Before that, we need docker images created (locally or pull it from the docker hub)
In my case, I will be pulling an image from DockerHub (react_django_demo_app)
# Dockerhub login command
$ docker login
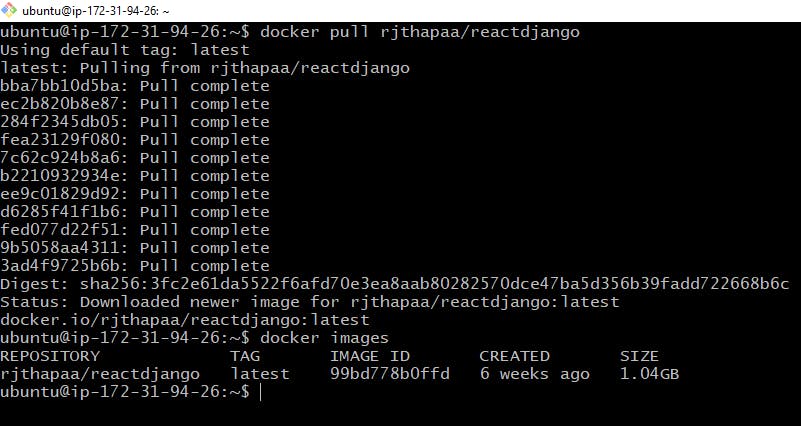
# Command to pull image from dockerHub
docker pull rjthapaa/reactdjango
Now create the service using the below command
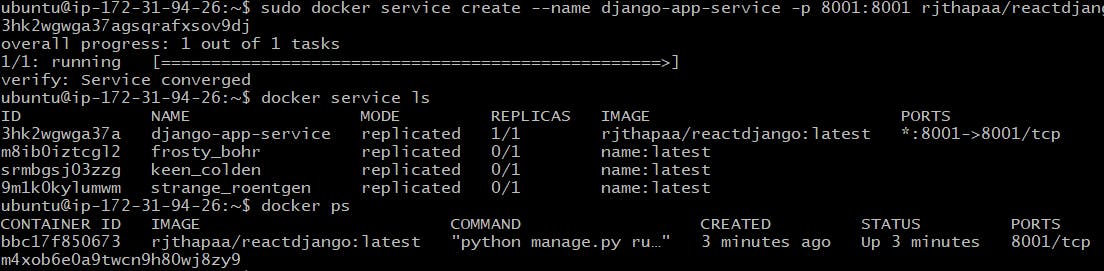
sudo docker service --name <service name> --replica 3 -p <hostport><containerport> <imagename>
sudo docker service create --name django-app-service -p 8001:8001 rjthapaa/reactdjango
Once the service is created
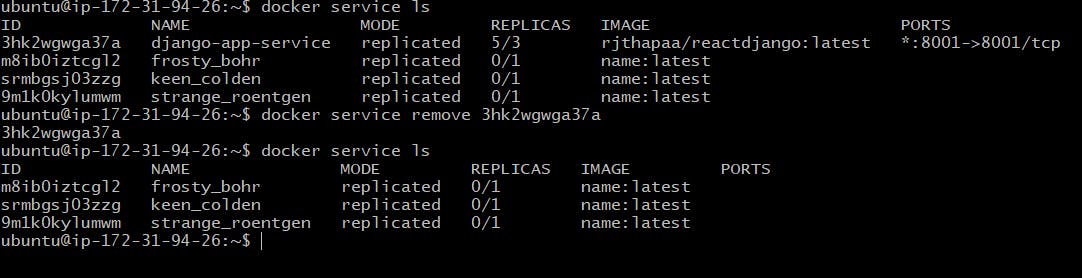
# check the service
$ docker service ls
# Check the container
$ docker ps
By default we have created a single replica of the container, to run the container as multiple replicas. We need to scale the docker service
# Scaling up the docker service
$ sudo docker service scale django-app-service=3
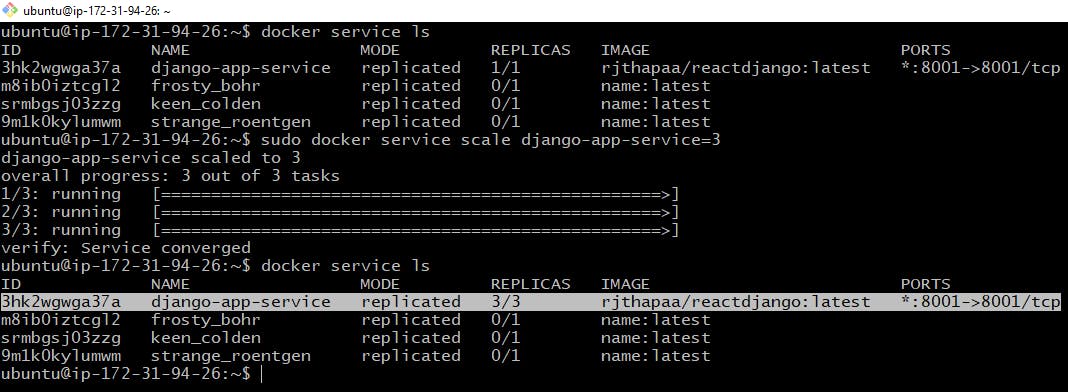
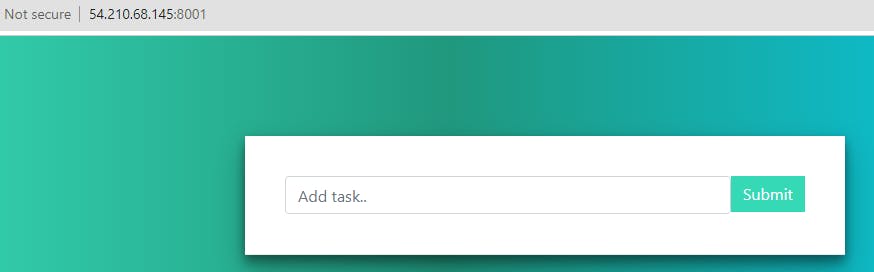
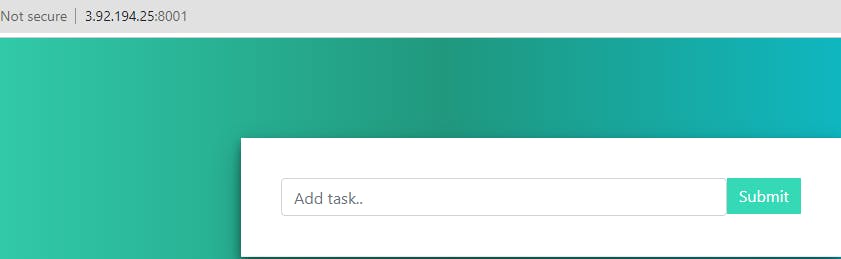
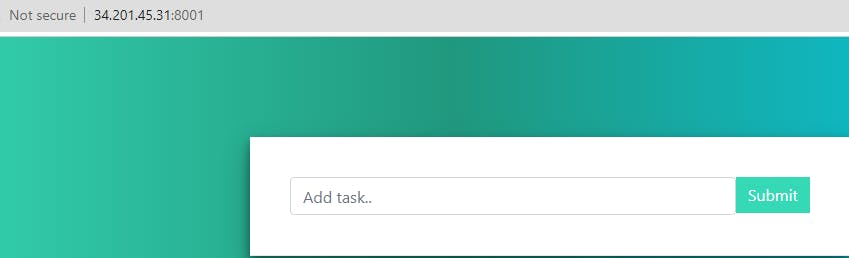
Now, this service will be running on all three nodes. To check this, just grab the Ip Address of any of the nodes followed by port 8001. As
<Any_PublicIP_of_3_VMS>:8001
Popular Docker Commands
# View, stop and delete running containers
$ docker ps
$ docker stop <container ID>
$ docker rm <container ID>
# View and delete docker Images
$ docker images
$ docker rmi <ImageID>
Docker Swarm commands
# info about the Node
$ docker info
# leaves the swarm cluster
$ docker swarm leave

On Docker_swarm-cluster
docker node ls
docker service remove <servicename>
Learn Minikube and kubectl here
Learn K8S kubeadm here
