What is Python
Python is a high-level programming language that is designed to be easy to read and write. It emphasizes simplicity and readability in its syntax, making it a popular choice for both beginners and experienced programmers. Python supports multiple programming paradigms, including procedural, object-oriented, and functional programming.
It's used for various tasks like web development, data analysis, automation, and more. Python code is easy to understand due to its clear syntax, making it a preferred choice for both beginners and experts.
How to Install Python On Windows and Linux?
a) For Windows Installation you can go to Python's official website python.org/downloads and Download Python 3.11.5 version (the latest version)
b) Python version is 3.11.5
c) You also can Install Visual Studio code to run Python script easily, as in VS Code the Python extension is also available which makes writing very easy.
d) From this website you can download code.visualstudio.com/download VS code as per your requirement.
Check the Python version, by typing python in the terminal or VSC
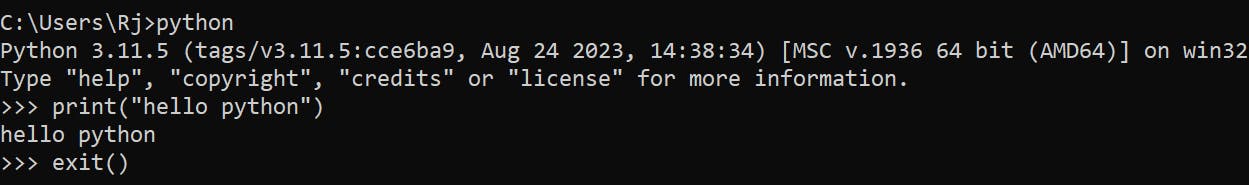
Let's start writing out the first Python code
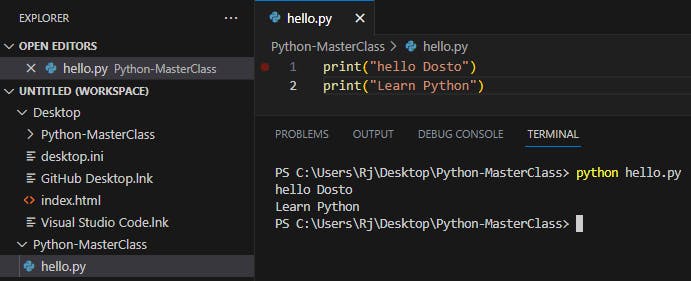
Example:1
print("Hello Dosto")
print("Learning python")
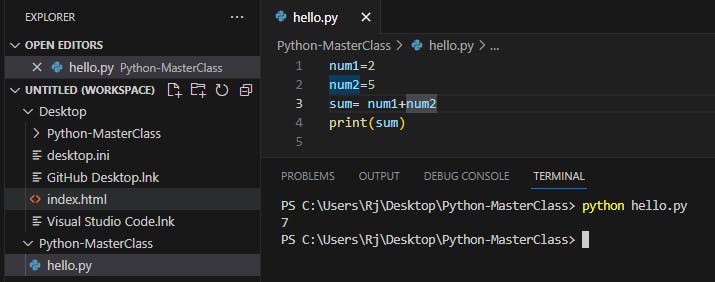
Example:2
Addition of two numbers
num1=2
num2=5
sum= num1+num2
print(sum)
Example 3:
Taking the values as input to perform calculator actions
num1=input("enter the number")
num2=input("enter the second number")
sum= num1+num2
print(sum)
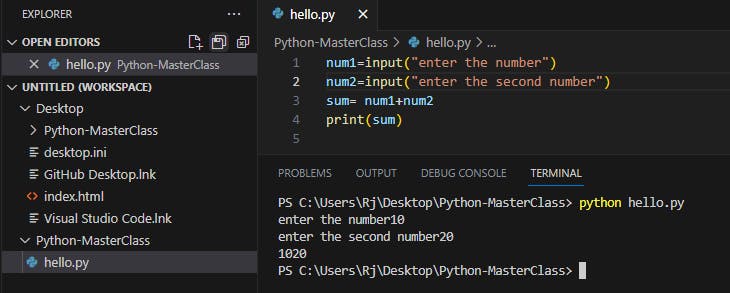
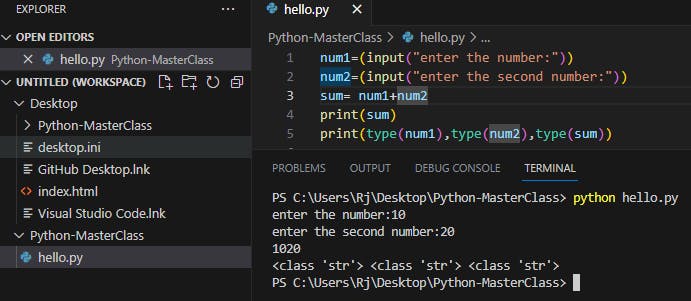
See the output in invalid for the addition operation, because here num1, num2 and sum are of string data type
How to check the data type of a variable
print(type(num1),type(num2),type(sum))
Now we will convert the data type from String to numeric (Int, float) by using typecasting
Typecasting
Converting one type of data type into another is called Typecasting
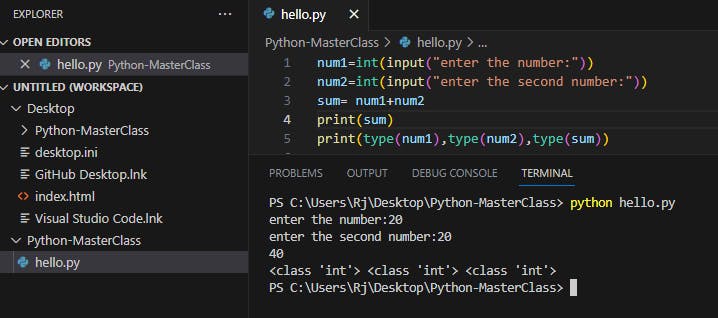
Add int or float before input followed by open and closed ()
num1=int(input("enter the number"))
num2=input(("enter the second number"))
sum= num1+num2
print(sum)
print(type(num1),type(num2),type(sum))
If you run the script now the data type is changed to numeric(int) and the sum is accurate
Example 3:
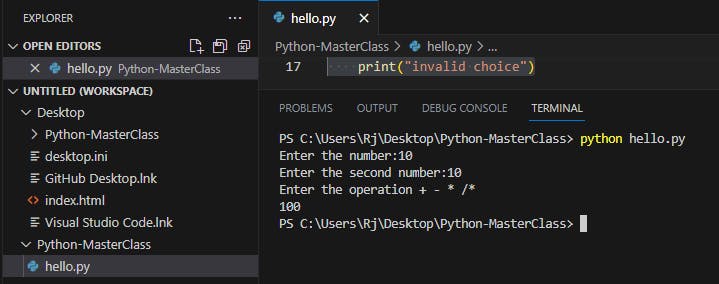
Taking the values as input to perform calculator actions by choice
num1=int(input("Enter the number:"))
num2=int(input("Enter the second number:"))
choice = input("Enter the operation + - * /")
if choice == "+":
sum= num1+num2
print(sum)
elif choice == "-":
diff= num1-num2
print(diff)
elif choice == "/":
div= num1/num2
print(div)
elif choice == "*":
mul=num1*num2
print(mul)
else:
print("invalid choice")
Data Structure and Algorithms In Python

Data Types | Classes | Description | |
String | str | Holds a sequence of characters | |
Numeric | int, float, complex | Holds numeric values | |
Boolean | bool | Holds either | |
Sequence | list, tuple, range | Holds a collection of items | |
Mapping | dict | Holds data in key-value pair form | |
Set | set, frozenness | Holds a collection of unique items |
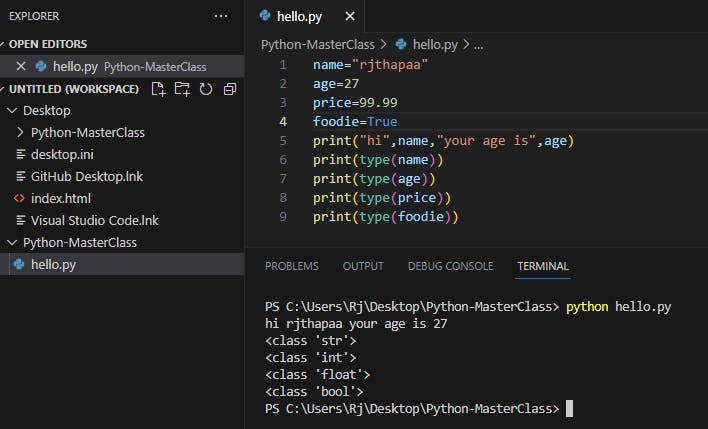
name="rjthapaa"
age=27
price=99.99
foodie=True
print("hi",name,"your age is",age)
print(type(name))
print(type(age))
print(type(price))
print(type(foodie))
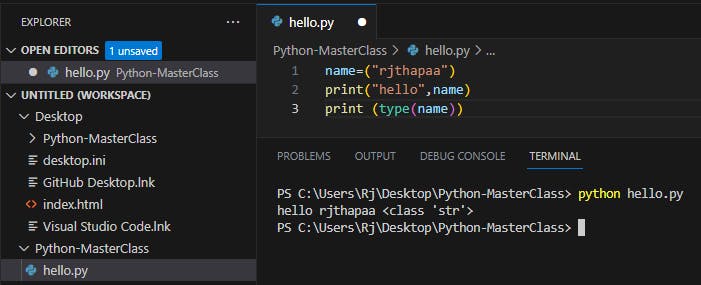
String Data Type:
name=("rjthapaa")
print("hello",name)
print (type(name))
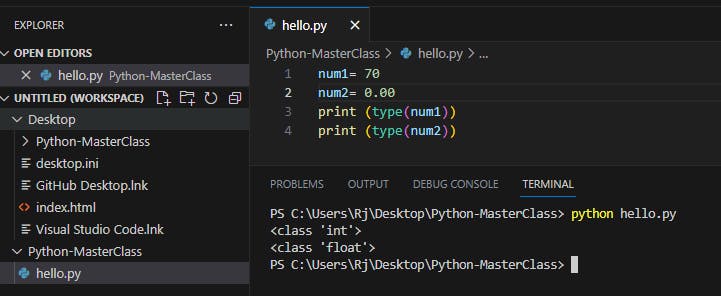
Numeric Data Type:
num1= 70
num2= 0.00
print (type(num1))
print (type(num2))
Sequence (List Data Type):
The list is a data structure, which can hold different types of data variables. Meanwhile, an array is a collection of data of a similar type.
A list is an ordered collection of similar or different types of items separated by commas and enclosed within brackets [ ].
Example1:
list_of_num= []
print(type(list_of_num))
Output: <class 'list'>
Example2:
list_of_num= []
list_of_num.append(1)
list_of_num.append(2)
list_of_num.append(["rjthapaa"])
print(list_of_num)
Output: [1,2,'rjthapaa']
Example3:
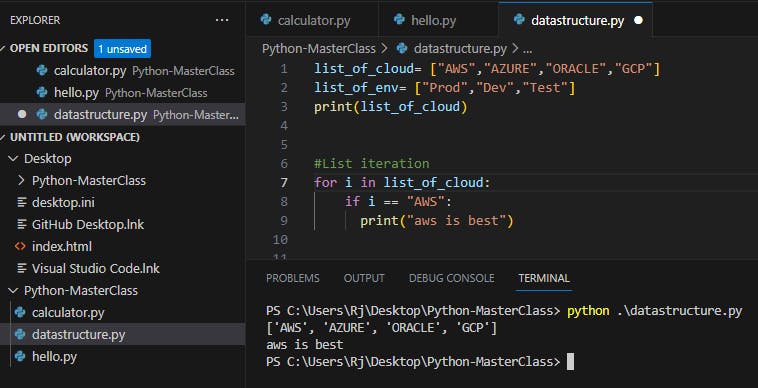
list_of_cloud= ["AWS","AZURE","ORACLE","GCP"]
list_of_env= ["Prod","Dev","Test"]
print(list_of_cloud)
print(list_of_cloud[0])
print(list_of_env[1])
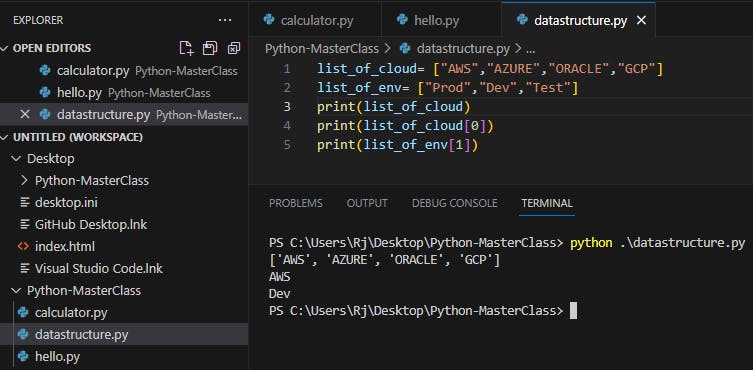
To access items from a list, we use the index number (0, 1, 2 ...)
Example 4:
list_of_cloud= ["AWS","AZURE","ORACLE","GCP"]
list_of_env= ["Prod","Dev","Test"]
print(list_of_cloud)
for i is list_of_cloud:
if i == "AWS":
print ("Aws is best cloud")
Tuple Data Type
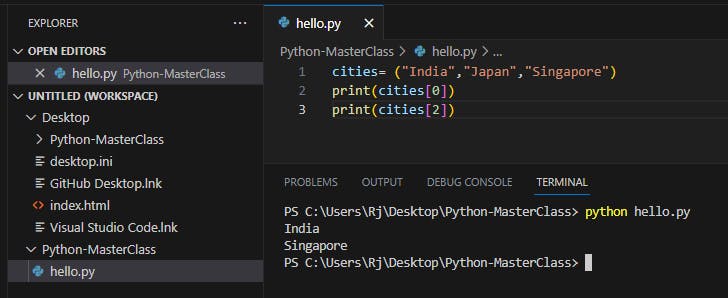
A tuple is an ordered sequence of items same as a list. The only difference is that tuples are immutable. Tuples once created cannot be modified.
We use the parentheses () to store items of a tuple.
cities= ("India","Japan","Singapore")
print(cities[0])
print(cities[2])
Mapping (Dictionary Data Type):
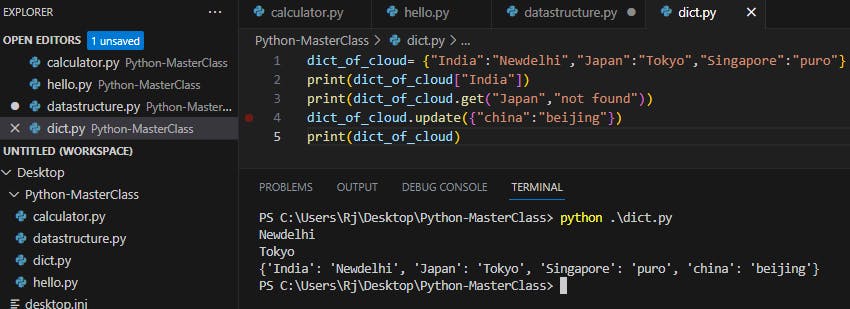
Python dictionary is an ordered collection of items. It stores elements in key/value pairs. Keys are unique identifiers that are associated with each value.
dict_of_cloud= {"India":"Newdelhi","Japan":"Tokyo","Singapore":"puro"}
print(dict_of_cloud["India"])
#print(dict_of_cloud.get("Japan","not found"))
dict_of_cloud.update({"china":"beijing"})
print(dict_of_cloud)
Set Data Type:
The Set is an unordered collection of unique items. Set is defined by values separated by
commas inside braces { }
Set_of_IDs= {112.113.114}
print(set_of_IDS)
print(type(set_of_IDS))
Output: 112,113.,114
<class 'set'>
